Road traffic injuries are a major public health problem and a leading cause of death and injury around the world. Each year nearly 1.2 million people die as a result of road clashes, and millions more are injured or disabled. This number is higher than deaths due to natural calamities or any contagious disease. Most of the victims of road accidents are vulnerable road users like pedestrians, cyclists and tow wheeler riders. In most cases, people killed and injured are men in the age group of 15 – 45 years which is known as productive age in any economy. The death results in loss of precious human resources in the country and total disaster for the families of the victims.
In Karnataka, about 10,000 people lose their lives and about 50,000 people are injured due to road accidents. Karnataka State is in 4th position in terms of road accident fatalities among Indian states.
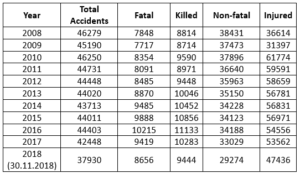
The following table provide details of accident fatalities and injuries for the last 10 years;
The causes of road accidents are due to the following reasons;
-
- Durnken Driving : One of the major cause of road accidents is drunken driving. The risk of being involved in the road accident is higher in case of drivers who consume alcohol even in small amount. The accidents by a drunken driver is generally due to poor judgment, slow reaction, delayed reflexes, poor visual attention, improper coordination and difficulty in identifying road bottlenecks. Consumption of alcohol also results in euphoric effect, thus making an individual shed his inhibitions and to violate traffic safety rules.
- Over speeding: Over speeding is one of the leading causes for the road accident in both developed as well as developing countries. According to National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), most of the road accidents in India were due to over speeding accounts for 43.70 percent of the total accidents which resulted in 69,969 deaths and 2,12,815 persons being injured.
- Driving without helmet: Motorcyclists are at high risk in traffic crashes, as per available data, wearing of helmets reduce the risk if head injury by around 69 per cent and death by around 42 per cent. Motorcyclists are more prone to crash injuries than car occupants because motorcycles are unenclosed, leaving riders vulnerable to contact with hard objects. Helment are highly effective in preventing brain injuries, which often require extensive and expensive treatment and may result in lifelong disability.
- Dangerous Driving: Dangerous driving practices such as wheeling, drag racing, driving on footpath, jumping signal lights etc., contribute road accidents in a big way especially in cities, drag racing and wheeling by youngsters results in fatalities.
Steps to improve safety on roads:
-
- Improve public education and communication to raise the awareness about the role of alcohol in accidents.
- Awareness programmes must focus on 25-40 years old, two wheeler drivers, heavy vehicle drivers and people drinking in bars and restaurants.
- Systematic training awareness programmes for bar tenders and restaurant owners to help them limit supply of alcohol to customers who are likely to drive after the drinks.
- Strict enforcement of laws prohibiting drunken driving.
- Steep penalties and jail sentence to drivers, who are caught with Blood Alcohol Content (BAC) level higher than permissible limit.
- Suspension or revocation of driving licenses of guilty drivers
- Promotion of vehicle devices that records and test drivers after they have been drinking.
- Random checks of drivers especially during night as a deterrence against drunken driving.
- Responsible employers with large fleets and many drivers should impose internal regulations on their staff to bring more discipline on roads.
- Introducing ride service programmes in hotels and restaurants for people who have consumed alcohol and may otherwise drive.
- Speed limits should be fixed scientifically for different categories of road depending on different functions of the road and its usage by various road users.
- While designing and developing roads, appropriate safe guards for vulnerable road users like pedestrians, cyclists and two wheeler riders should be incorporated.
- Appropriate visible signages needs to be erected for better information of road users.
- Installation of speed governors for all public transport vehicles and goods vehicles should be mandatory at the manufacturing stage itself.
- Automatic speed enforcement devices such as speed cameras and speed interceptors should be deployed by enforcement agencies on all highways and city roads.
- Increased public awareness and improving compliance towards speed restrictions needs to be given importance through campaigns and public education programmes.
- Ensure compliance to Helmet Rule for both drivers and pillion riders.
CONCLUSION:
Road safety cannot be achieved by enforcement alone. Apart from bringing the violators to penalty, awareness programmes to educate citizens should be undertaken. Non-Governmental Organizations and civil society should join hands with enforcement agencies to evolve effective strategies to ensure greater safety on roads.